What is PD-1 and PD-L1?
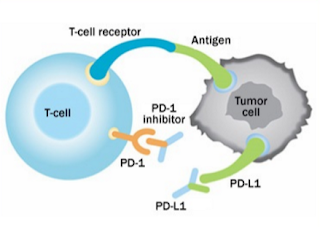
PD-1 refers to Programmed Death 1, which is an important immunology inhibitor, a member of CD28 super family. PD-1 targeted immunology modulation has been quite vital in anticancer, antiinflammation, antirejection rose from organ transplant etc. Its ligand, PD-L1 has the same effect as a checkpoint inhibitor.
PD-L1 stands for Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1, which is a type I 40kDa transmembrane protein. In normal situation, immune system will fight against foreign antigens that accumulate in the lymph or spleen and promote antigen-specific T cells proliferation. When PD-1 is bound to PD-L1, it helps keep T cells from killing other cells, including cancer cells.
Some anticancer drugs, called immune checkpoint inhibitors, are used to block PD-1. When this protein is blocked, the “brakes” on the immune system are released and the ability of T cells to kill cancer cells is increased.
What are the roles of PD-1 and PD-L1 in cancer?
In most cases, the immune system undergoes a series of steps which lead to an anticancer immune response and cancer cell death. This is known as the cancer immunity cycle:
1. Mutated antigens produced by tumor cells are captured by dendritic cells.
2. The dendritic cells prime T cell with tumor antigen and stimulate the activation of cytotoxic T cells.
3. Activated T cells then travel to the tumor and infiltrate the tumor environment.
4. The activated T cells recognize and bind to the cancer cells.
5. The bound effector T cells release cytotoxins, which induce apoptosis in their target cancer cells.
How PD-1 and PD-L1 fight against cancer in immunotherapy?
Monoclonal antibody therapies targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 are being now routinely used in cancer administration. Such therapies include Nivolumab (an anti-PD-1 drug developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb), Pembrolizumab, another anti-PD1 drug (developed by Merck).
Similar methods are being used targeting PD-L1 to treat other cancer types, for example, non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, renal cell carcinoma and bladder cancer.
Representatives of drug PD-1
Ÿ Pembrolizumab (trade name—Keytruda) works as an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy to help fight certain cancers. It may be used when your melanoma has spread or cannot be removed by surgery (advanced melanoma), or It may be used to help prevent melanoma from coming back after it and lymph nodes that contain cancer have been removed by surgery.
Ÿ OPDIVO (nivolumab) is a prescription medicine used to treat people with a type of advanced stage lung cancer (called non-small cell lung cancer) that has spread or grown and you have tried chemotherapy that contains platinum, and it did not work or is no longer working.
Representatives of drug PD-L1
Ÿ TECENTRIQ (Atezolizumab) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma.
Ÿ IMFINZI (Durvalumab) is a prescription medicine used to treat a type of lung cancer called non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Experimental drug
At least two PD-L1 inhibitors are in the experimental phase of development:
Ÿ BMS-936559, by Bristol-Myers Squibb
Ÿ CK-301, by Checkpoint Therapeutics
Reference
1. Jun Gong, Alexander Chehrazi-Raffle, Srikanth Reddi and Ravi Salgia, Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations, Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, 2018