Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a complex mental health condition that can develop after a person experiences a traumatic event or series of events. These events could range from combat exposure and accidents to assault, natural disasters, or any situation that causes intense fear, helplessness, or horror. The aftermath of such events can disrupt an individual's mental and emotional well-being, leading to a range of distressing symptoms. Fortunately, there are several effective approaches to treating PTSD and helping individuals reclaim their sense of peace and stability.
1. Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, plays a crucial role in PTSD treatment. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is among the most commonly used approaches. This therapy helps individuals understand and reframe negative thought patterns and beliefs related to the traumatic event. Exposure therapy, a type of CBT, involves gradually exposing the person to reminders of the traumatic event in a safe and controlled environment, helping them desensitize and reduce the emotional distress associated with these reminders.
2. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a unique therapeutic approach specifically designed to address trauma-related issues. During EMDR sessions, individuals recall their traumatic memories while focusing on bilateral stimulation, which can involve moving their eyes back and forth or receiving tactile stimuli. This process helps the brain reprocess the traumatic memories in a way that reduces their emotional impact, allowing individuals to form healthier associations with these memories.
3. Medication: Medications can also be a valuable component of PTSD treatment. Antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are commonly prescribed to help manage symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and intrusive thoughts. These medications work by balancing neurotransmitter levels in the brain, helping individuals regain emotional stability and improving their overall quality of life.
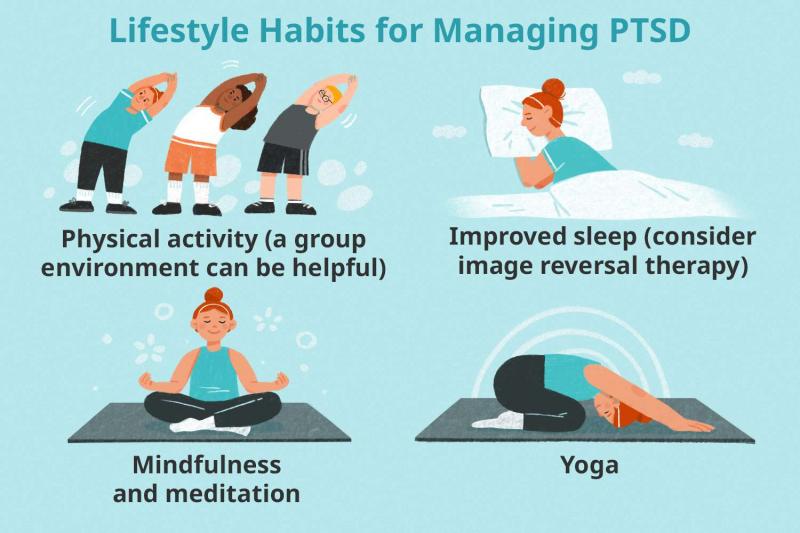
4. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can be highly effective in managing the symptoms of PTSD. These techniques help individuals stay present and reduce feelings of anxiety and hyperarousal. Mindfulness allows individuals to observe their thoughts and emotions without judgment, fostering a sense of self-awareness and emotional regulation.
5. Support Groups: Support groups provide a safe space for individuals with PTSD to connect with others who have experienced similar trauma. Sharing experiences and insights with people who understand their struggles can be immensely healing. Support groups foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation, helping individuals realize they are not alone in their journey toward recovery.
6. Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly contribute to PTSD recovery. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and avoiding substances like alcohol and drugs can enhance overall well-being and resilience. Engaging in activities that bring joy and a sense of accomplishment can also improve mood and reduce stress.
In conclusion, "Reclaiming Peace: Effective Approaches to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Treatment" highlights various strategies that have proven successful in helping individuals overcome the debilitating effects of PTSD. A comprehensive approach that combines psychotherapy, medication, mindfulness, and lifestyle changes can empower individuals to gradually regain control over their lives and find a renewed sense of peace. It's important to remember that each person's journey toward healing is unique, and finding the right combination of approaches under the guidance of mental health professionals is key to achieving lasting recovery from PTSD.