Kyphoplasty and Percutaneous Discectomy: Minimally Invasive Techniques for Spinal Disorders
Kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy are two advanced and minimally invasive procedures used to treat specific spinal disorders. These innovative techniques have revolutionized the management of conditions such as vertebral compression fractures and herniated discs, providing patients with quicker recovery times, reduced pain, and improved quality of life. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the principles, procedures, indications, benefits, and potential risks of kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy.
Understanding Kyphoplasty
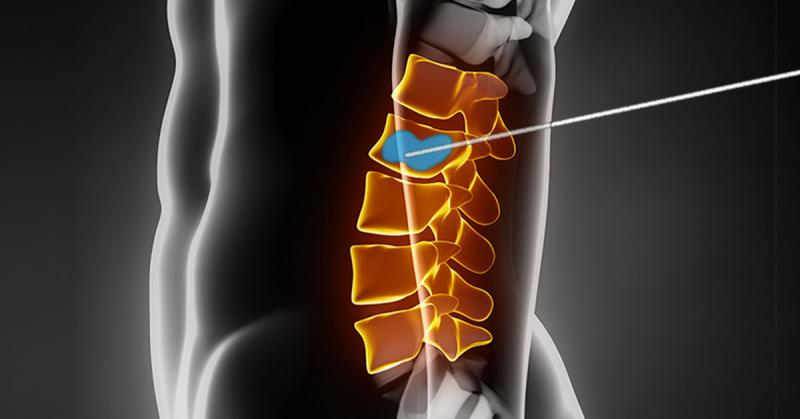
Kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure performed to treat painful vertebral compression fractures, commonly caused by osteoporosis or trauma. The goal of kyphoplasty is to stabilize the fractured vertebra, relieve pain, and restore vertebral height.
The procedure involves the following steps:
-
Guided Needle Insertion: Under fluoroscopic guidance, a hollow needle is carefully inserted into the fractured vertebra.
-
Balloon Inflation: A deflated balloon is introduced through the needle into the fractured area. Once in position, the balloon is inflated, creating a cavity and restoring vertebral height.
-
Cement Injection: After the balloon is deflated and removed, medical-grade bone cement is injected into the cavity to stabilize the fractured vertebra.
Kyphoplasty not only provides immediate pain relief but also helps prevent further collapse of the affected vertebra and restores spinal alignment.
Understanding Percutaneous Discectomy
Percutaneous discectomy, also known as percutaneous disc decompression or percutaneous endoscopic discectomy, is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat herniated discs that cause nerve compression and radicular pain. Unlike traditional open surgeries, percutaneous discectomy involves accessing the herniated disc through a small incision or needle, minimizing tissue damage and reducing the risk of complications.
The procedure involves the following steps:
-
Incision or Needle Insertion: A small incision is made, or a needle is inserted through the skin, guiding a thin tube (cannula) to the affected disc.
-
Endoscope Insertion: An endoscope, a slender tube with a camera and light source, is introduced through the cannula, providing the surgeon with a clear view of the herniated disc.
-
Discectomy: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon removes the herniated portion of the disc, relieving pressure on the compressed nerve root.
Percutaneous discectomy allows for a quicker recovery, reduced postoperative pain, and a lower risk of complications compared to traditional open discectomy.
Indications for Kyphoplasty and Percutaneous Discectomy
Kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy are indicated for specific spinal conditions:
Kyphoplasty Indications:
-
Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: Kyphoplasty is commonly used to treat painful vertebral fractures resulting from osteoporosis or low bone density.
-
Traumatic Vertebral Fractures: Kyphoplasty may be employed to stabilize vertebral fractures caused by trauma or injury.
Percutaneous Discectomy Indications:
-
Herniated Disc: Percutaneous discectomy is indicated for herniated discs that cause nerve compression and result in radicular pain, sciatica, or leg pain.
-
Bulging Disc: It may also be used to treat bulging discs that compress nearby nerves and cause symptoms.
Benefits of Kyphoplasty and Percutaneous Discectomy
Both kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy offer several advantages over traditional open surgeries:
-
Minimally Invasive: These procedures involve small incisions or needle insertions, reducing tissue damage and scarring.
-
Shorter Recovery Time: Patients typically experience shorter hospital stays and quicker postoperative recovery.
-
Reduced Pain: Minimally invasive techniques often result in less postoperative pain compared to open surgeries.
-
Improved Quality of Life: By stabilizing fractures and relieving nerve compression, patients can experience significant pain relief and improved mobility.
-
Lower Risk of Complications: Minimally invasive procedures are associated with a lower risk of infection and other complications compared to open surgeries.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy are generally safe and effective, there are some potential risks and considerations to be aware of:
-
Fracture Recurrence: Kyphoplasty may not prevent future fractures in other vertebrae, especially in individuals with osteoporosis.
-
Allergic Reactions: Some patients may experience allergic reactions to the bone cement used in kyphoplasty.
-
Nerve Injury: While rare, there is a slight risk of nerve injury or infection associated with the use of needles or endoscopes in percutaneous discectomy.
-
Patient Selection: Not all patients are suitable candidates for these procedures, and individual evaluation is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Conclusion
Kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy represent significant advancements in the field of spinal surgery, offering minimally invasive alternatives to traditional open procedures for specific spinal conditions. With their ability to provide rapid pain relief, improve spinal stability, and enhance patients' quality of life, these techniques have become valuable tools in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures and herniated discs. By combining technological innovation with specialized surgical skills, kyphoplasty and percutaneous discectomy continue to pave the way for safer, more efficient, and patient-centric spinal interventions.