Introduction
When it comes to respiratory diseases, many are familiar with well-known conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, there's a lesser-known but equally concerning group of disorders known as interstitial lung diseases (ILD). These diseases affect the interstitium, the tissue and space around the air sacs in the lungs. Unlike other respiratory illnesses, ILDs can be elusive, creeping into our lives quietly and causing irreversible damage. In this blog, we will explore what ILD is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of early intervention.
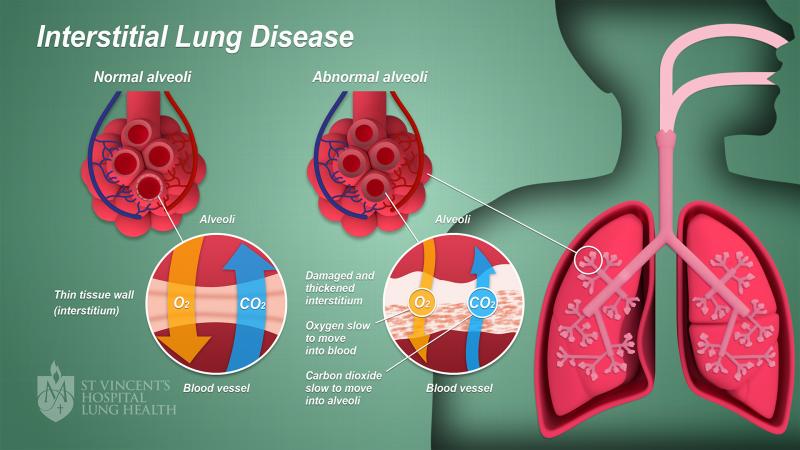
What is Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)?
ILD is a broad term encompassing a group of disorders characterized by inflammation and scarring of the interstitium. The interstitium is a crucial part of the lungs responsible for gas exchange, and when it becomes damaged, it hinders the ability of the lungs to transport oxygen efficiently. The damage is often progressive, leading to impaired lung function and potentially fatal consequences.
Types and Causes
ILD is an umbrella term for various lung diseases, each with unique causes. Some of the common types include:
-
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF): The most prevalent and severe form of Interstitial Lung Disease, IPF has no apparent cause, hence the term "idiopathic." It mainly affects older individuals.
-
Sarcoidosis: This ILD results from the formation of small lumps of cells in different body organs, including the lungs. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be related to the immune system.
-
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: This condition arises from inhaling substances like mold spores, animal dander, or certain chemicals. It triggers an inflammatory response in the lungs.
-
Connective Tissue Disease-Associated ILD: Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic sclerosis can lead to ILD.
-
Occupational Lung Diseases: Prolonged exposure to harmful substances like asbestos or coal dust can cause ILD.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of ILD can be vague and often mistaken for other respiratory issues. It's crucial to recognize these warning signs early on:
-
Persistent Dry Cough: A chronic, non-productive cough is one of the first signs of ILD.
-
Shortness of Breath: Gradual onset of breathlessness, especially during physical activity.
-
Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired, even after minimal exertion.
-
Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss may occur as the disease progresses.
-
Joint Pain: In certain types of ILD, joint pain and swelling may be present.
Diagnosis and Prognosis
Diagnosing ILD is challenging and requires a comprehensive approach. A thorough medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, imaging (chest X-ray or CT scan), and sometimes a lung biopsy may be necessary. An early and accurate diagnosis is vital, as ILD can progress rapidly, leading to irreversible lung damage and reduced life expectancy.
Treatment Options
While ILD has no cure, several treatments can slow down its progression and manage symptoms:
-
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and antifibrotic agents may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and scarring.
-
Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen can help improve oxygen levels in the blood and alleviate breathlessness.
-
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A program involving exercise, breathing techniques, and counseling to improve lung function and overall well-being.
-
Lung Transplant: In severe cases, a lung transplant may be considered for eligible patients.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early detection and intervention can significantly impact the outcome of ILD. If you or your loved ones experience any persistent respiratory symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. Raising awareness about ILD is crucial to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate care.
Conclusion
Interstitial Lung Disease may be lesser-known, but its impact on individuals and families can be devastating. Understanding the symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and exploring appropriate treatment options are essential steps towards managing this challenging condition. By increasing awareness and research efforts, we can improve the lives of those affected by ILD and work towards better outcomes for the future.