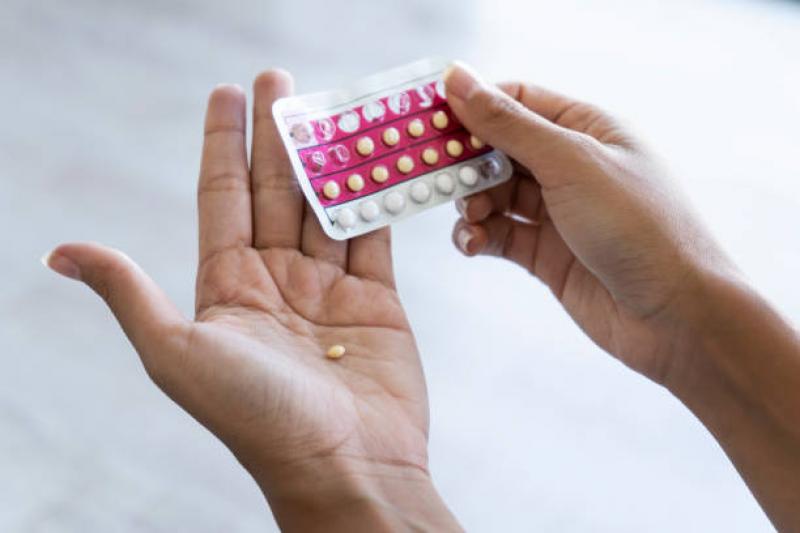
Hormonal contraceptives have played a transformative role in empowering women to take control of their reproductive health and family planning. These contraceptive methods, which use synthetic hormones to prevent pregnancy, offer a safe and effective means of contraception. Since the introduction of the first oral contraceptive pill in the 1960s, hormonal contraceptives have evolved significantly, offering a diverse range of options to suit individual needs and preferences. This article explores the mechanisms, types, benefits, and considerations associated with hormonal contraceptives, highlighting their impact on women's lives and reproductive choices.
Understanding Hormonal Contraceptives: How They Work
Hormonal contraceptives use synthetic hormones to mimic and regulate the natural hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle. Most hormonal contraceptives work by preventing ovulation, inhibiting the release of an egg from the ovaries. They also thicken cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg. Additionally, hormonal contraceptives alter the uterine lining, making it less receptive to a fertilized egg, thus preventing implantation.
Types of Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives come in various forms, catering to diverse preferences and medical considerations. The most common types include:
-
Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs): These pills contain a combination of estrogen and progestin hormones and are taken daily. COCs are highly effective when used correctly.
-
Progestin-Only Pills (Mini-pills): Mini-pills contain only progestin hormones and are suitable for women who cannot take estrogen-containing pills.
-
Hormonal Patch: The patch is applied to the skin and releases hormones into the bloodstream over a week, after which it is replaced with a new one.
-
Vaginal Ring: The vaginal ring is a flexible ring inserted into the vagina, releasing hormones over a month.
-
Injectable Contraceptives: These contraceptives are administered as a shot and provide protection for several weeks or months.
-
Hormonal Implants: Small rods implanted under the skin release hormones and provide protection for several years.
-
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Some IUDs release hormones and provide long-term protection, while others are non-hormonal.
Benefits of Hormonal Contraceptives
Hormonal contraceptives offer several advantages beyond their primary role in preventing pregnancy. Some of the key benefits include:
-
High Effectiveness: When used correctly, hormonal contraceptives are highly effective in preventing unwanted pregnancies.
-
Regulating Menstrual Cycles: Hormonal contraceptives can help regulate menstrual cycles, reducing symptoms of irregular, painful, or heavy periods.
-
Reduced Risk of Certain Cancers: Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives has been associated with a reduced risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers.
-
Acne Management: Certain hormonal contraceptives can improve acne in some individuals by reducing androgen production.
-
Protection Against Ovarian Cysts: Hormonal contraceptives can help prevent the formation of ovarian cysts.
-
Convenience and Privacy: Many hormonal contraceptives offer discreet and convenient options for family planning, allowing women to manage their reproductive health privately.
Considerations and Side Effects
While hormonal contraceptives offer numerous benefits, they may not be suitable for everyone, and side effects can vary among individuals. Common side effects include nausea, breast tenderness, mood changes, and breakthrough bleeding. Women with specific medical conditions, such as a history of blood clots, heart disease, or certain cancers, may need to avoid certain types of hormonal contraceptives. It is essential for healthcare providers to conduct thorough medical evaluations and discuss potential risks and benefits before prescribing hormonal contraceptives.
Empowering Women's Reproductive Choices
Hormonal contraceptives have been instrumental in giving women greater control over their reproductive choices. By providing reliable and reversible methods of birth control, women can plan pregnancies according to their life goals and circumstances. Hormonal contraceptives have also contributed to empowering women economically, socially, and academically by allowing them to pursue education and careers on their terms.
Addressing Misconceptions and Myths
Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, misconceptions and myths persist in some communities. Disseminating accurate information and dispelling misconceptions is essential to ensuring that women can make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
Ongoing Research and Advancements
Research in reproductive health continues to drive advancements in contraceptive options. Efforts are underway to develop new formulations with improved side effect profiles and non-daily dosing regimens. Additionally, innovative approaches, such as male hormonal contraceptives and reversible methods for long-term protection, are being explored.
Conclusion
Hormonal contraceptives have been a transformative force in women's reproductive health, offering a spectrum of options for contraception and menstrual regulation. By providing women with greater agency over their reproductive choices, hormonal contraceptives have facilitated educational and career opportunities, improved family planning, and contributed to the overall well-being of women worldwide. As research and technology progress, the future of hormonal contraceptives holds the promise of even safer, more convenient, and effective options, empowering women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and lives.