Dermatomyositis, though rare, is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects both the skin and muscles, causing significant challenges for those diagnosed with the condition. This enigmatic disease often poses diagnostic difficulties and requires a multidisciplinary approach for effective management. In this blog, we will delve into what dermatomyositis is, its symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options.
Understanding Dermatomyositis: Dermatomyositis is a rare inflammatory condition that falls under the umbrella of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies—a group of disorders characterized by muscle inflammation. While the exact cause of dermatomyositis remains unknown, it is believed to be an autoimmune disease, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its tissues, leading to inflammation.
Symptoms and Presentation: Dermatomyositis typically presents with a combination of skin and muscle symptoms. Some common signs and symptoms include:
-
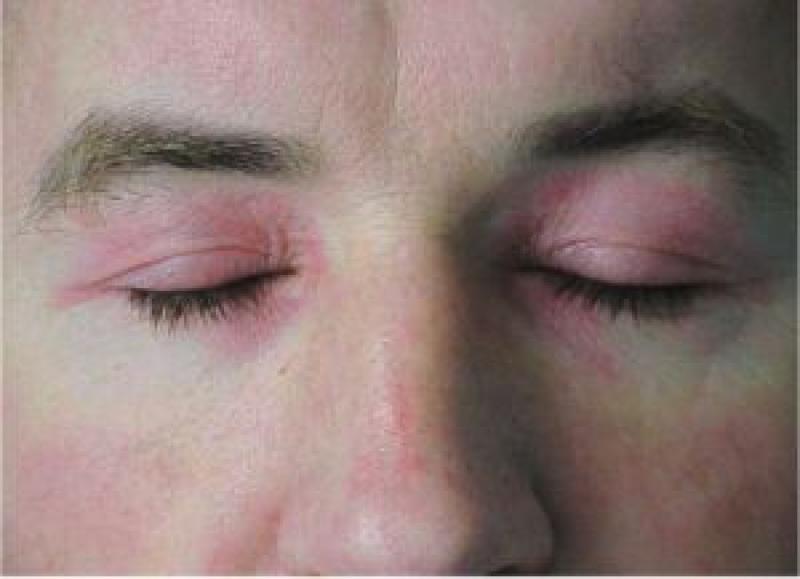
Skin Changes: The disease often manifests with distinctive skin rashes, especially on the face (heliotrope rash) and the knuckles (Gottron's papules). The skin may appear reddish or purplish, and it can be sensitive, itchy, or painful.
-
Muscle Weakness: Progressive muscle weakness is a hallmark of dermatomyositis. Patients may experience difficulty in performing everyday tasks, such as getting up from a chair or lifting objects.
-
Joint Pain: Joint pain and inflammation are also common in dermatomyositis, affecting the wrists, elbows, knees, and other joints.
-
Systemic Involvement: In some cases, dermatomyositis may affect other organs, leading to symptoms such as lung inflammation, difficulty swallowing, or heart involvement.
Diagnosis and Management: Diagnosing dermatomyositis can be challenging due to its variable presentation and overlap with other conditions. A thorough evaluation by a rheumatologist and dermatologist is essential. Diagnostic tests may include:
-
Muscle Enzyme Levels: Blood tests to measure muscle enzymes (e.g., creatine kinase) that are released into the bloodstream when muscle damage occurs.
-
Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin tissue may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of characteristic changes.
-
Electromyography (EMG): This test measures electrical activity in muscles, helping to assess muscle function and detect abnormalities.
-
MRI or Muscle Biopsy: These tests may be used to evaluate muscle inflammation and rule out other muscle diseases.
Treatment Options: Dermatomyositis is typically treated with a combination of medications and physical therapy to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications. Treatment may involve:
-
Corticosteroids: High-dose corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment to suppress inflammation.
-
Immunosuppressive Medications: Additional medications that suppress the immune system may be used, especially if the disease is severe or not responding to steroids alone.
-
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises can help maintain muscle strength and improve mobility.
-
Sun Protection: Since sun exposure can worsen skin symptoms, using sunscreen and protective clothing is crucial.
Conclusion: Dermatomyositis may be a rare and complex disease, but early diagnosis and appropriate management can lead to improved outcomes and a better quality of life for those affected. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment approaches, the medical community continues to unravel the mysteries surrounding this condition, providing hope for more effective therapies in the future. If you or a loved one experience any symptoms suggestive of dermatomyositis, seeking prompt medical attention and consultation with specialists is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.