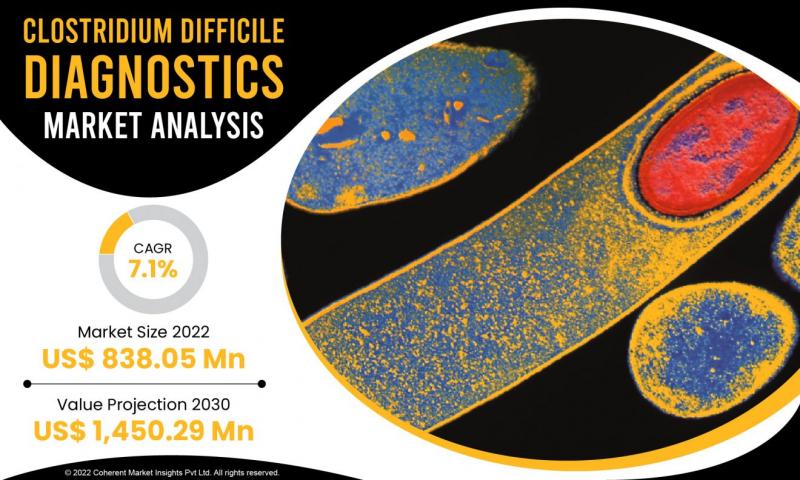
Clostridium difficile, commonly known as C. difficile or C. diff, is a bacterium that can cause infections in the colon, leading to a range of symptoms, from mild diarrhea to life-threatening conditions. The diagnostics and treatment of C. difficile infections have seen significant advancements in recent years. This blog will explore the latest developments in the Clostridium difficile diagnostics and treatment market.
Diagnostics:
- Molecular Diagnostics: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing has become the gold standard for C. difficile diagnostics. It offers high sensitivity and specificity, enabling accurate detection of the bacteria's DNA in stool samples.
- Toxin Testing: Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) are still commonly used to detect C. difficile toxins in stool samples. However, they are less sensitive than molecular diagnostics and may produce false negatives.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): NGS technologies are emerging as a powerful tool for C. difficile strain typing and understanding the genetic diversity of the bacterium. This can aid in tracking outbreaks and understanding resistance patterns.
- Point-of-Care Testing: Rapid diagnostic tests that can be performed at the patient's bedside are gaining popularity. These tests provide quick results, allowing for prompt treatment initiation.
Treatment:
- Antibiotics: The cornerstone of C. difficile treatment remains antibiotics. Metronidazole, vancomycin, and fidaxomicin are commonly prescribed drugs. However, the choice of antibiotic may depend on the severity of the infection and previous treatment history.
- Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT): FMT involves transferring healthy donor stool into the patient's colon to restore the balance of gut bacteria. It has shown promising results, especially for recurrent C. difficile infections that do not respond to antibiotics.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies like bezlotoxumab and actoxumab have been developed to prevent recurrent C. difficile infections by neutralizing the toxins produced by the bacterium.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are being studied for their potential to prevent C. difficile infections by promoting a healthy gut microbiome. However, their effectiveness is still under investigation.
Market Trends:
The Clostridium difficile diagnostics and treatment market is expected to witness continued growth due to the rising incidence of C. difficile infections, increased awareness, and advancements in diagnostic technologies and treatment options. Key market trends include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment approaches based on an individual's microbiome and antibiotic susceptibility is gaining attention.
- Telemedicine: The use of telemedicine for C. difficile diagnosis and follow-up care is on the rise, especially in remote or underserved areas.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research efforts aim to develop novel antibiotics, probiotics, and therapeutic approaches to combat C. difficile infections more effectively.
- Infection Control: Hospitals and healthcare facilities are investing in infection control measures to prevent C. difficile outbreaks, including improved hand hygiene and environmental cleaning.
Conclusion:
The Clostridium difficile diagnostics and treatment market has seen significant progress in recent years, with molecular diagnostics, FMT, monoclonal antibodies, and other innovative approaches reshaping the landscape of C. difficile management. As research continues and healthcare practices evolve, we can expect further improvements in the diagnosis and treatment of C. difficile infections, ultimately benefiting patients and healthcare systems worldwide.
Read More….