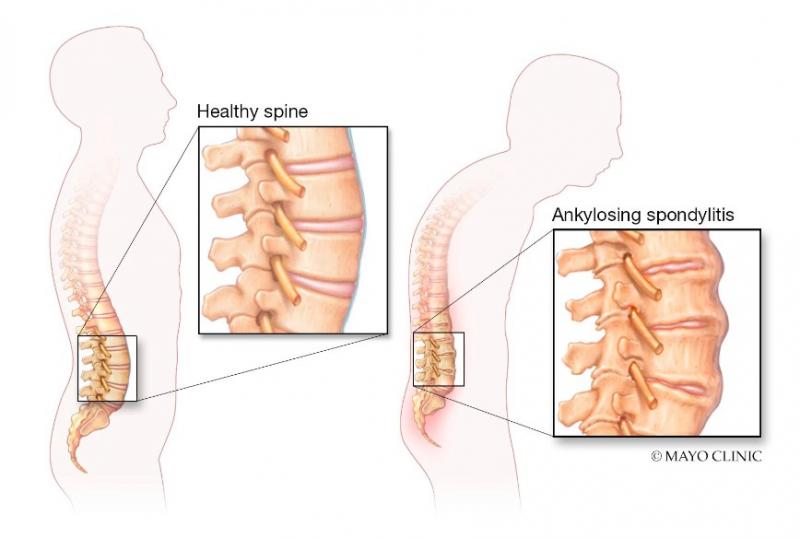
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While it may not be as well-known as other autoimmune diseases, AS can have a profound impact on the lives of those living with it. In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of AS, shedding light on the challenges faced by individuals battling this invisible and often misunderstood condition.
- Understanding Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of arthritis that mainly affects the axial skeleton, which includes the spine and sacroiliac joints. The condition leads to inflammation, fusion, and eventual stiffening of the affected joints, making it difficult for the patient to move and perform everyday activities. AS typically begins in early adulthood, with men being more susceptible than women.
- Signs and Symptoms
The early symptoms of AS can be subtle and may include back pain and stiffness, which is often more pronounced in the morning or after periods of inactivity. As the disease progresses, the pain and stiffness can extend to the neck, hips, and other joints, impacting a person's ability to move freely. Fatigue, inflammation in the eyes (uveitis), and chest pain due to involvement of the rib cage are other possible symptoms.
- Causes and Diagnosis
The exact cause of Ankylosing Spondylitis is still not fully understood, but it is believed to have a strong genetic component, with the HLA-B27 gene being a significant risk factor. Environmental factors may also play a role in triggering the disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Diagnosing AS can be challenging since its early symptoms may be mistaken for other back-related issues. X-rays, MRIs, and blood tests are commonly used to aid in the diagnosis.
- Impact on Mental Health
Living with AS goes beyond the physical limitations; it can significantly impact a person's mental well-being. The chronic pain, uncertainty about the future, and the challenges of managing a chronic illness can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Support from friends, family, and mental health professionals is crucial in helping patients cope with these emotional struggles.
- Treatment and Management
While there is currently no cure for AS, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy and regular exercise can help maintain flexibility and prevent joint stiffness. In more severe cases, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic therapies may be recommended.
- The Importance of Exercise
Regular physical activity is vital for individuals with AS. Exercise helps to maintain joint flexibility, improve posture, and strengthen the muscles around the affected joints. Swimming, yoga, and low-impact exercises are particularly beneficial for AS patients. However, it's essential to tailor the exercise routine to each individual's specific needs and limitations.
- Coping Strategies and Support
Living with AS can be challenging, but a strong support system can make a significant difference. Joining support groups or online communities allows individuals with AS to connect with others who understand their struggles. Sharing experiences, tips, and advice can provide emotional support and foster a sense of belonging.
Conclusion
Ankylosing Spondylitis is an invisible battle that affects countless individuals around the world. While it may not receive as much attention as other autoimmune diseases, its impact on physical and mental health is profound. Raising awareness and understanding about AS is crucial in providing better support and care for those living with this condition. By promoting early diagnosis, encouraging regular exercise, and fostering a supportive environment, we can empower individuals with AS to live fulfilling lives despite the challenges they face.