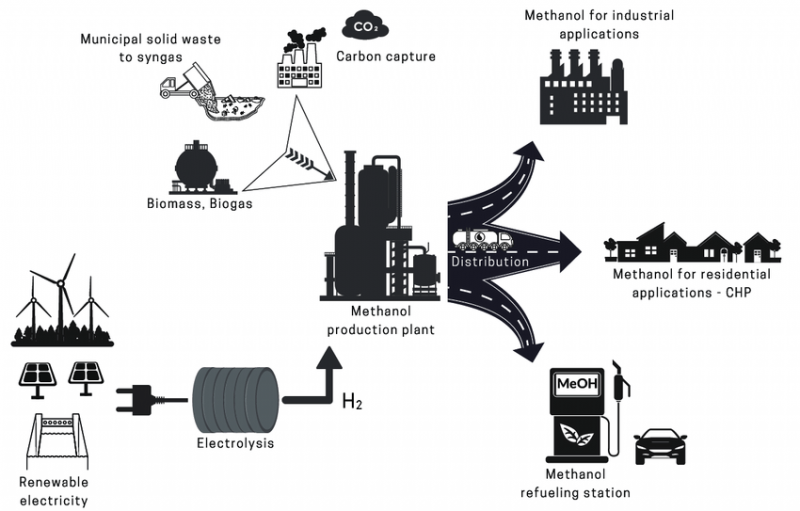
In the quest for a greener and more sustainable future, renewable energy sources play a pivotal role. One such source that is gaining significant attention is renewable methanol. Methanol, also known as wood alcohol, has long been used as an essential industrial chemical, but its traditional production processes heavily rely on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. However, with advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainable practices, renewable methanol is emerging as a promising alternative.
Understanding Renewable Methanol: Renewable methanol is produced using renewable feedstocks such as biomass, carbon dioxide (CO2) from various sources, or hydrogen generated through electrolysis using renewable electricity. This makes it a carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative fuel, depending on the production method. Unlike conventional methanol derived from fossil fuels, renewable methanol can be harnessed from waste materials like agricultural residues, wood waste, and even CO2 captured from industrial processes or directly from the atmosphere.
Benefits of Renewable Methanol:
-
Reduced Carbon Footprint: By utilizing carbon dioxide that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere, renewable methanol helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions. It effectively closes the carbon loop by converting CO2 back into a usable fuel.
-
Energy Storage and Transportation: Renewable methanol offers promising solutions for energy storage and transportation. It can be used in fuel cells or converted back to electricity, making it a versatile option to store excess renewable energy for times of high demand or low supply.
-
Drop-in Fuel: One of the key advantages of renewable methanol is its compatibility with existing infrastructure and engines. It can be used as a drop-in replacement for conventional methanol, gasoline, and diesel, without significant modifications to engines or distribution systems.
-
Enhancing Energy Security: As a domestically producible fuel, renewable methanol can reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and promoting economic stability.
-
Circular Economy: By utilizing waste materials or capturing CO2, renewable methanol fosters the principles of a circular economy. It transforms waste into a valuable resource and promotes a more sustainable approach to resource management.
Applications of Renewable Methanol: The applications of renewable methanol are diverse and far-reaching:
-
Transportation: It can power cars, trucks, ships, and aircraft, serving as a renewable alternative to conventional fossil fuels.
-
Chemical Industry: Renewable methanol can be used as a feedstock for the production of various chemicals and materials, including plastics, adhesives, and solvents.
-
Power Generation: It can be utilized in fuel cells to generate electricity, providing a clean energy option for various applications.
-
Cooking and Heating: Renewable methanol can be used for cooking and heating, reducing reliance on traditional fuels like wood and charcoal, which can cause indoor air pollution.
Challenges and the Road Ahead: Despite its immense potential, renewable methanol faces challenges in terms of scalability and cost-effectiveness. The technology to capture and utilize CO2 is still evolving, and large-scale production facilities are required to make the process economically viable. Additionally, while progress has been made, the renewable energy sector needs continued support from governments, industries, and consumers to drive innovation and investment in this field.
Conclusion: Renewable methanol is a promising avenue for the transition towards a sustainable energy landscape. Its ability to utilize waste materials and CO2 to produce a clean fuel that can be integrated into existing systems makes it a valuable player in the fight against climate change. With sustained efforts in research, development, and policy support, renewable methanol could become a key component in achieving a greener and more sustainable future for generations to come.