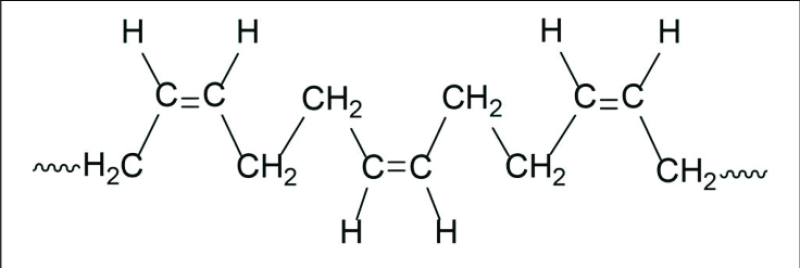
Polybutadiene, a synthetic rubber polymer, plays a critical role in various industries due to its unique chemical structure and physical properties. Created through the polymerization of 1,3-butadiene monomers, this elastomer is widely recognized for its superior wear resistance, low temperature flexibility, and excellent abrasion resistance. The global demand for polybutadiene continues to expand, driven primarily by the automotive sector and manufacturing industries. Understanding the chemical nature, application spectrum, and dynamics related to polybutadiene is essential for stakeholders looking to navigate this evolving landscape effectively.
Chemical and Physical Characteristics Defining Polybutadiene Performance
Polybutadiene molecular structure consists of long chains made up of repeating butadiene units, giving it exceptional elasticity. It exhibits a low glass transition temperature, typically around -80°C, which allows it to remain flexible in extremely cold environments. This physical trait makes it an essential material in applications where durability and flexibility under harsh climatic conditions are required. Furthermore, polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and tear compared to other elastomers, resulting from its low hysteresis and excellent resilience. In addition to its role as a standalone material, polybutadiene is frequently blended with styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) or natural rubber to enhance performance characteristics, especially in tire manufacturing. The polymer’s ability to resist crack propagation is another vital attribute, contributing to its use in high-stress environments.
Key Industrial Applications Driving Polybutadiene Growth Globally
The most significant application of polybutadiene is in the production of tires, where it improves tread wear and extends tire life. Passenger vehicle tires, truck and bus tires, and even motorcycle tires often incorporate polybutadiene to achieve better performance metrics. Beyond tire manufacturing, polybutadiene finds usage in automotive parts, such as suspension bushings and seals, where flexibility and resistance to mechanical stress are critical. Additionally, the polymer is employed in golf balls, where it acts to enhance elasticity and energy return, resulting in better distance and control. Polybutadiene’s application extends to the production of conveyor belts, hoses, and various molded goods requiring high abrasion resistance. Its role in impact modifiers for plastics and as a core material in adhesives and sealants underscores its versatility. The polymer’s excellent electrical insulating properties also open opportunities in the electronics and electrical appliances industries.
Commercial Overview and Investment Trends in Polybutadiene Manufacturing Sector
The commercial viability of polybutadiene manufacturing is closely linked to raw material availability, primarily butadiene derived from crude oil and natural gas refining processes. Fluctuating feedstock prices directly influence production costs, affecting downstream pricing and profitability for polybutadiene users and producers alike. Recent trends indicate growing investments in bio-based butadiene production methods, aiming to reduce environmental impact and stabilize supply. Manufacturing facilities increasingly adopt advanced polymerization technologies, such as solution and emulsion polymerization, to improve product uniformity and performance characteristics. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and capacity expansions characterize the sector’s commercial landscape, emphasizing global players’ efforts to consolidate share. Furthermore, demand from emerging economies continues to stimulate capacity enhancements, as urbanization and industrialization accelerate automotive and industrial goods production. The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) also creates new usage patterns for polybutadiene in EV tire compounds and other specialized components, diversifying opportunities and influencing investment decisions.
Polybutadiene remains a pivotal material across multiple industrial domains due to its unmatched combination of mechanical properties and versatility. A robust understanding of its characteristics, application trends, and dynamics is vital for manufacturers, investors, and end-users aiming to capitalize on this growing polymer segment.
Get This Report in Japanese Language - ポリブタジエン
Get This Report in Korean Language - 폴리부타디엔
Read More Articles Related to this Industry –
Sustainable Agrochemicals: Innovations for Eco-friendly Farming
Types of Agrochemicals and Their Role in Modern Farming
About Author:
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement.
(LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)