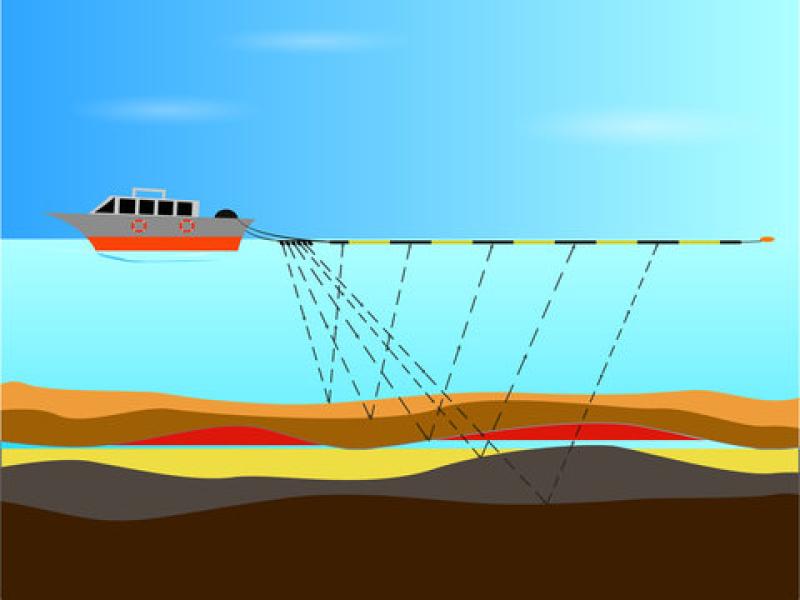
Seismic surveys have become an indispensable tool in subsurface exploration and geological analysis, playing a critical role in discovering natural resources such as oil, gas, and minerals. These surveys use controlled seismic waves to map underground rock formations, providing detailed insights into the earth’s subsurface structure. By analyzing how the seismic waves reflect off different rock layers, experts can create highly accurate images of subsurface geology, helping industries make informed decisions. The importance of seismic survey techniques extends beyond the energy sector, impacting environmental studies, construction projects, and disaster preparedness through precise ground assessment.
Advanced Seismic Survey Technologies Used in Hydrocarbon Exploration
The Seismic Survey has witnessed rapid technological advancements, improving the accuracy and efficiency of subsurface imaging. Techniques like 2D and 3D seismic surveys enable extensive data acquisition, allowing precise interpretation of geological structures beneath the earth’s surface. Three-dimensional seismic surveys, in particular, provide volumetric images, offering a clearer view of prospective hydrocarbon reservoirs. Additionally, 4D seismic surveys—time-lapse seismic monitoring—track changes within reservoirs during production, which assists in optimizing extraction strategies. Modern equipment includes seismic sources such as vibroseis trucks and air guns, combined with sensitive geophones or hydrophones for wave detection. These innovations have revolutionized hydrocarbon exploration by reducing drilling risks and increasing success rates.
Seismic Survey Applications Across Various Industrial Sectors
While traditionally associated with oil and gas exploration, seismic surveys are now utilized in numerous industries requiring subsurface knowledge. In mining, seismic methods help identify ore bodies and monitor mine stability. Civil engineering projects rely on seismic surveys to evaluate ground conditions for the construction of buildings, bridges, and tunnels, ensuring safety and structural integrity. Environmental and geotechnical studies use seismic data to assess natural hazards like fault lines, landslides, and earthquake-prone zones. This multidisciplinary application highlights the versatility of seismic survey methodologies and their value in promoting sustainable development and risk mitigation.
Economic Impact and Commercial Use of Seismic Data in Resource Management
Seismic survey data plays a pivotal commercial role in resource management by reducing exploration costs and increasing the accuracy of drilling locations. Access to detailed subsurface information minimizes the likelihood of dry wells and improves the overall efficiency of resource extraction. The commercial benefit extends to investors and operators, as seismic information directly influences decision-making and budgeting within exploration projects. Additionally, seismic data is increasingly packaged as a service or product offered by specialized firms, providing valuable datasets for multiple stakeholders in the energy sector. As the demand for cleaner energy sources grows, seismic surveys also contribute to identifying viable sites for geothermal energy exploitation, reflecting their expanding commercial significance.
Navigational Resource for In-depth Seismic Survey Market Analysis and Trends
Detailed market research reports are essential for understanding ongoing trends and future opportunities within the seismic survey industry. Such reports offer comprehensive insights into market dynamics, competitive landscapes, technology advancements, and regional demand factors. For businesses and analysts interested in exploring the seismic survey sector, accessing curated databases and analytical publications provides strategic guidance for investment and operational decisions. These navigational tools cover segments such as equipment types, surveying techniques, end-user industries, and geographic breakdowns, making them indispensable for stakeholders seeking to capitalize on market shifts and innovations.
Emerging Innovations Transforming Future Seismic Survey Capabilities
The future of seismic surveys is being shaped by cutting-edge innovations aimed at improving data quality, reducing operational costs, and minimizing environmental impact. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are increasingly integrated into seismic data processing, enabling faster and more accurate interpretation. Autonomous seismic survey units and drones are being developed to conduct surveys in difficult or remote terrains, enhancing field data collection efficiency. Additionally, integrated multi-physics surveys that combine seismic with electromagnetic or gravity data provide more comprehensive subsurface pictures. Sustainable practices, including low-impact seismic sources, address ecological concerns and regulatory demands, steering the industry toward greener solutions. These technological advancements promise to redefine how seismic surveys support resource exploration and earth sciences.
Global Demand Dynamics and Competitive Landscape Analysis in Seismic Survey Sector
Global seismic survey demand is influenced by factors such as fluctuating oil prices, government regulations on exploration activities, and technological progress. Regions rich in hydrocarbon reserves remain the primary markets, while new exploration initiatives in frontier areas are emerging. The competitive landscape includes major service providers offering turnkey seismic solutions and innovative proprietary technologies. Strategic partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions characterize the sector as companies strive to enhance capabilities and market reach. Pricing models, service customization, and technological differentiation are key competitive factors influencing client choices. Keeping abreast of these market developments is critical for entities aiming to sustain growth and innovation in this dynamic industry.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations Impacting Seismic Survey Operations
Despite its benefits, seismic surveying faces several operational challenges and regulatory scrutiny. Environmental concerns arise from the potential disturbance caused by seismic sources, particularly in sensitive ecosystems and marine habitats. Regulatory frameworks increasingly require detailed environmental impact assessments and adherence to noise and vibration limits. Furthermore, access to land or sea for conducting surveys often involves negotiations with governments and local communities. Technical challenges include dealing with complex geology, data volume management, and ensuring high-resolution imaging in challenging subsurface conditions. Overcoming these obstacles requires robust planning, community engagement, and continuous technological improvements to balance exploration needs with environmental stewardship.
Get this Report in Japanese Language: 地震調査
Get this Report in Korean Language: 지진 탐사
Read More Articles Related to this Industry
Types of Biofuels: Exploring the Future of Renewable Energy
About Author:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163)