What is Chondroitin Sulfate?
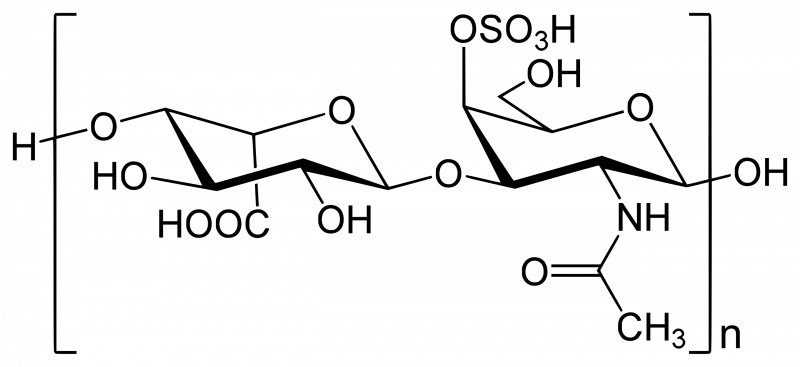
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid). Chondroitin sulfate is found in cartilage, providing it with resistance to compression. It helps attract water and proteoglycans to maintain proper cartilage density and resilience, absorbing shock and protecting bone surfaces in joints. Chondroitin is the word referring to all cartilage tissues. Sulfate refers to its sulfate radical (SO3H) functional groups which are added on during the body's biosynthesis of the compound.
Sources of Chondroitin Sulfate
Chondroitin Sulfate occurs naturally in vertebrate animals, especially in cartilage and connective tissue. It is extracted from bovine, porcine, or shark cartilage and salmon ear cartilage. Bovine cartilage is one of the most common sources used to produce pharmaceutical and nutritional supplements containing chondroitin sulfate. Shark and chicken sternum have also been utilized as sources for commercial chondroitin sulfate.
The Human Diet and Supplementation
Humans cannot synthesize significant amounts of chondroitin sulfate, so it must be obtained through the diet or supplements. Traditionally, people received adequate amounts from eating meat, poultry, fish, and cartilage. However, modern meat production and food processing methods remove cartilage. As a result, dietary intake of chondroitin sulfate from normal eating is relatively low. Many adults take chondroitin sulfate supplements, alone or combined with other ingredients like glucosamine, to support joint health. Typical daily supplement doses range between 400-1,200 mg.
Potential Health Benefits of Chondroitin Sulfate
Osteoarthritis Management: There is substantial evidence that chondroitin sulfate supplements can help reduce osteoarthritis symptoms like knee pain, stiffness, and physical disability. It appears to protect cartilage and inhibit enzymes that break cartilage down. Studies show chondroitin sulfate therapy improves joint space narrowing compared to placebo.
CV Health: Some research links higher dietary chondroitin sulfate intake with reduced risk of heart attack, stroke and cardiovascular mortality, possibly by inhibiting inflammation and oxidation involved in atherosclerosis. However, evidence from supplements is still limited.
Skin Aging: Preliminary animal and test tube research found chondroitin sulfate may help improve skin elasticity and hydration by stimulating collagen and hyaluronic acid production in skin fibroblasts. This suggests a potential anti-aging effect, but well-designed human studies are still needed.
Brain Health: Animal research shows chondroitin sulfate has neuroprotective properties. It appears to inhibit inflammation in the brain and decrease beta-amyloid plaque accumulation related to Alzheimer's disease. More research is warranted, but it may someday contribute to strategies for preventing cognitive decline.
Research on Precautions and Side Effects
Chondroitin sulfate is generally well tolerated with few reported side effects at recommended doses. However, it can potentially interact with some medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) used for arthritis as both work to reduce inflammation. Additionally, there is a lack of research on chondroitin sulfate use during pregnancy or breastfeeding, so it is prudent to avoid supplementation without physician guidance. Allergic reactions are rare, but possible in sensitive individuals. Consult a doctor before use if taking anticoagulant drugs due to chondroitin sulfate's potential anti-platelet activity. Overall, doses up to 1,200 mg daily appear safe when taken as directed.
Potential Applications Beyond Dietary Supplements
Tissue Engineering: Studies show chondroitin sulfate can promote cell adhesion and growth in three-dimensional tissue engineering scaffolds intended to repair cartilage damage or other tissues. This highlights its potential as a biomaterial for regenerative procedures.
Pharmaceutical Aid: As a component of proteoglycans important in many tissues, chondroitin sulfate has been investigated as an excipient for drug delivery systems. It appears to enhance absorption of some medications applied topically or delivered directly to joints. This exemplifies its utility beyond human nutrition.
In summary, chondroitin sulfate is a naturally occurring compound important for cartilage structure and resilience. It shows promise for managing osteoarthritis and may offer additional health benefits currently under investigation. More research continues to unravel chondroitin sulfate's roles and shed light on any precautions needed with supplementation. Commercial applications also utilize its properties in tissue engineering and pharmaceutical formulations. Overall, chondroitin sulfate deserves ongoing study as a potentially advantageous nutrient and therapeutic agent.
Get More Insights On Chondroitin Sulfate