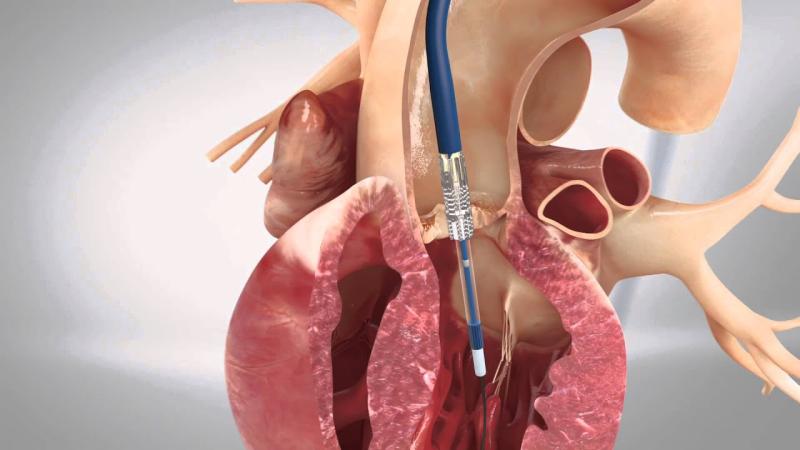
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI), also known as Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR), has revolutionized the treatment of aortic stenosis, particularly for patients at high or intermediate risk for conventional surgical procedures. This minimally invasive approach offers a life-saving alternative by replacing the diseased aortic valve without the need for open-heart surgery. Over the past decade, continual technological improvements and expanding clinical indications have driven widespread adoption of TAVI across different patient populations globally.
Technological Innovations Driving Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
Recent advancements in catheter design, valve materials, and delivery systems have made Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation safer and more efficient. Early-generation devices faced challenges such as paravalvular leak, vascular complications, and limited patient eligibility due to anatomical constraints. However, newer generation valves incorporate enhanced sealing skirts to minimize leaks and feature improved flexibility and deliverability to accommodate complex vasculature. These innovations have also enabled smaller profile introducer sheaths, reducing procedural trauma and bleeding risk.
Additionally, imaging techniques such as 3D echocardiography and computed tomography angiography play a critical role in patient selection and procedural planning. Real-time imaging guidance during TAVI procedures ensures precise valve deployment, decreasing the incidence of complications and improving overall clinical outcomes. Advances in hemodynamic monitoring and post-procedural care protocols are also contributing to shorter hospital stays and faster patient recovery.
Emerging Trends in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
The TAVI market is experiencing rapid growth driven by increased awareness of minimally invasive valvular therapies and a growing aging population susceptible to aortic stenosis. Expanding clinical trial data demonstrate comparable or superior efficacy and safety of TAVI relative to surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in low-risk patients, further broadening the eligible patient base. This shift is stimulating greater adoption by hospitals and cardiology centers worldwide.
Key trends shaping the TAVI landscape include the development of next-generation valves tailored for younger and lower-risk patients, integration of artificial intelligence in procedural planning, and growing emphasis on durability and long-term valve performance. Additionally, reimbursement policies and regulatory approvals in emerging markets are facilitating wider access to TAVI technologies. The rise of hybrid operating rooms equipped for both surgical and catheter-based interventions is also enhancing procedural versatility.
Commercial Applications and Expanding Patient Access for Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation
TAVI’s commercial growth is closely linked to evolving indications, including treatment of bicuspid aortic valves, valve-in-valve procedures for failing bioprosthetic valves, and expanding use in low-risk cohorts. The procedure has become an integral offering in cardiovascular centers focused on structural heart disease. As procedural safety and efficacy improve, healthcare providers increasingly incorporate TAVI into their service portfolios, enhancing patient access.
Device manufacturers continue investing in commercialization strategies focused on educating clinicians, facilitating training programs, and establishing robust post-market surveillance systems. Additionally, reimbursement expansion under governmental and private insurance schemes is improving affordability and availability. Dedicated TAVI heart teams comprising interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, and anesthesiologists ensure optimal patient outcomes and support volume growth.
Transactional Considerations Impacting Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Adoption
The procedural cost and infrastructure requirements of TAVI influence adoption rates in various healthcare settings. Hospitals must invest in specialized equipment, trained personnel, and appropriate surgical backup to offer comprehensive TAVI services. As technology matures and device costs decrease, wider adoption is feasible even in mid-sized cardiology centers.
Payors and healthcare policy makers play a critical role by defining coverage criteria based on clinical evidence and cost-effectiveness analyses. Transactional considerations also include sourcing agreements with device suppliers and cartridge disposal protocols in catheterization labs. Value-based care models focusing on patient-reported outcomes after TAVI are gaining traction, encouraging higher quality standards and cost containment.
Get This Report in Japanese Language - 経カテーテル大動脈弁留置術
Get This Report in Korean Language - 경피적 대동맥판막 이식술
Read More Articles Related to this Industry –
Nanofiber Applications in Medical Devices: Revolutionizing Healthcare
Camera Modules in Medical Devices: Revolutionizing Diagnostics and Treatment
About Author:
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement.
(LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)