Advancements in Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Reconstruction Devices: Improving Outcomes for Patients
Introduction:
Injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) are common among athletes and individuals involved in physically demanding activities. These injuries can significantly impact an individual's mobility and lead to long-term joint instability. To address these issues, medical advancements have led to the development of sophisticated ACL and PCL reconstruction devices, revolutionizing the treatment and rehabilitation process. This blog explores the key aspects of these devices, their benefits, and how they are improving patient outcomes.
- Understanding ACL and PCL Injuries:
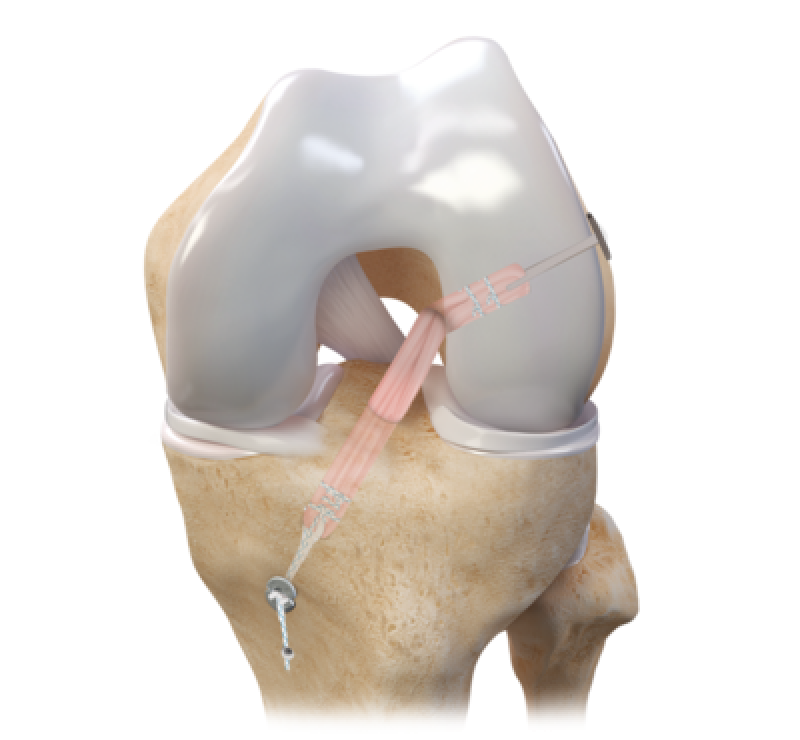
Before delving into the advancements in reconstruction devices, it is essential to understand the role of the ACL and PCL in the knee joint. The ACL prevents the tibia (shinbone) from sliding too far forward, while the PCL prevents excessive backward movement. Injuries to these ligaments often occur during abrupt deceleration, pivoting, or direct impact, resulting in painful and unstable knees.
- Traditional Reconstruction Techniques:
Traditionally, ACL and PCL reconstruction involved autografts or allografts sourced from the patient's own body or a donor, respectively. While effective, these procedures had limitations, such as limited graft availability, donor site morbidity, and the risk of graft rejection.
- Advancements in ACL and PCL Reconstruction Devices:
a. Bioabsorbable Implants: Bioabsorbable implants are a significant advancement in ACL and PCL reconstruction. These implants are made from materials that gradually dissolve over time, allowing for natural tissue healing while providing initial stability to the injured ligament. They eliminate the need for second surgeries to remove metal hardware, reducing the risk of complications.
b. Anatomically Contoured Grafts: Advancements in imaging and 3D printing technologies have facilitated the creation of anatomically contoured grafts. These grafts mimic the natural shape of the ACL and PCL, improving surgical precision and promoting better graft integration. As a result, patients experience reduced post-operative pain and faster recovery.
c. Ligament Augmentation and Reconstruction System (LARS): The Ligament Augmentation and Reconstruction System (LARS) is a synthetic ligament made from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. LARS provides an alternative to traditional grafts and has shown promising results in ACL and PCL reconstructions, offering greater strength and durability.
d. Double-Bundle Technique: The double-bundle technique involves reconstructing both the anteromedial and posterolateral bundles of the ACL. This technique more closely replicates the natural function of the ligament, leading to improved knee stability and overall joint performance.
- Benefits and Outcomes:
a. Faster Recovery and Rehabilitation: The use of advanced reconstruction devices has significantly shortened the recovery period for ACL and PCL injuries. Patients can return to daily activities and sports more quickly, reducing the time away from their active lifestyles.
b. Enhanced Knee Stability: Advanced reconstruction devices provide better knee stability, reducing the risk of subsequent injuries and improving the patient's overall quality of life.
c. Lower Complication Rates: Bioabsorbable implants and anatomically contoured grafts have lowered the risk of complications such as infection, graft failure, and hardware-related issues.
d. Improved Long-Term Results: With the latest techniques and devices, patients are experiencing better long-term outcomes, with higher success rates and a lower likelihood of requiring revision surgeries.
Conclusion:
Advancements in ACL and PCL reconstruction devices have revolutionized the treatment of ligament injuries, providing patients with faster recovery times, improved knee stability, and better long-term outcomes. As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations in this field, further enhancing the quality of life for individuals recovering from ACL and PCL injuries. It is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals to stay updated with these advancements to ensure optimal treatment and rehabilitation strategies are utilized.