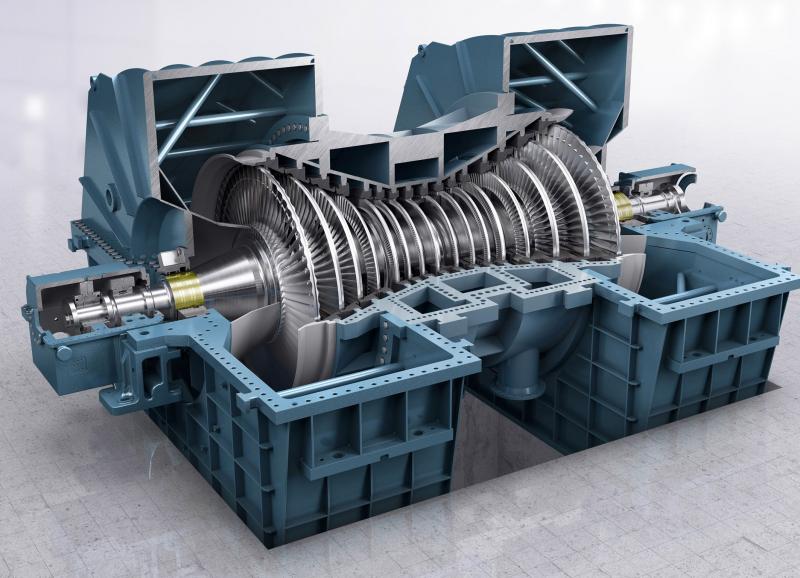
Steam turbines have been a cornerstone of the global power generation industry for over a century. These remarkable machines harness the power of steam to produce electricity efficiently and reliably, serving as a crucial component in various power plants and industrial applications. The Steam Turbine Market continues to evolve, adapting to changing energy needs and advancing technologies while remaining a driving force behind the world's power generation.
Unraveling the Mechanism: How Steam Turbines Work
At its core, a steam turbine operates on a simple principle: the conversion of thermal energy in steam into mechanical energy, which is then used to generate electricity. Steam is produced by heating water through various means, such as burning coal, natural gas, nuclear fission, or harnessing renewable sources like geothermal or solar energy.
The high-pressure steam is then directed into the steam turbine's blades, causing them to spin. As the steam expands and loses pressure, it imparts its energy onto the blades, setting the turbine rotor in motion. This rotational motion is then transmitted to an electricity generator, converting mechanical energy into electrical power.
Diverse Applications of Steam Turbines
Steam turbines find extensive application across a range of industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and reliability. They are a common sight in power plants, where they serve as the main drivers for electricity generation in fossil-fuel power plants, nuclear power plants, and some renewable energy plants. Additionally, steam turbines play a crucial role in combined-cycle power plants, where they work in conjunction with gas turbines to maximize energy output.
Beyond power generation, steam turbines also find use in various industrial processes, such as refining, chemical production, and petrochemical manufacturing. They serve as drivers for pumps, compressors, and other rotating equipment, contributing to the smooth functioning of these industries.
Market Dynamics: Embracing Efficiency and Sustainability
In recent years, the Steam Turbine Market has experienced significant changes driven by the global focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. The push for cleaner energy sources has led to the development of advanced steam turbine technologies that increase efficiency, reduce emissions, and optimize power generation.
Research and development efforts have resulted in innovations such as advanced steam cycle designs, improved blade materials, and enhanced turbine control systems. These advancements have led to higher efficiency levels, enabling power plants to generate more electricity with reduced fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its continued relevance and adaptability, the steam turbine industry faces several challenges. One of the primary challenges is the competition from alternative power generation technologies, such as wind turbines and solar panels. These renewable energy sources have gained popularity due to their environmentally friendly nature and decreasing costs, posing competition for traditional power generation methods.
Nevertheless, the Steam Turbine Market also presents opportunities for growth, particularly in emerging economies where the demand for electricity is rapidly increasing. Additionally, the ongoing development of more efficient and sustainable steam turbine technologies enables existing power plants to undergo upgrades and improve their performance, extending their operational life and reducing their environmental impact.
Conclusion
The Steam Turbine Market continues to play a significant role in powering the world, delivering electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. With advancements in technology and a commitment to sustainability, steam turbines remain a reliable and efficient source of power generation. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the steam turbine industry will persistently strive to meet the global demand for electricity while minimizing its environmental footprint, ensuring a greener and more sustainable future for generations to come.