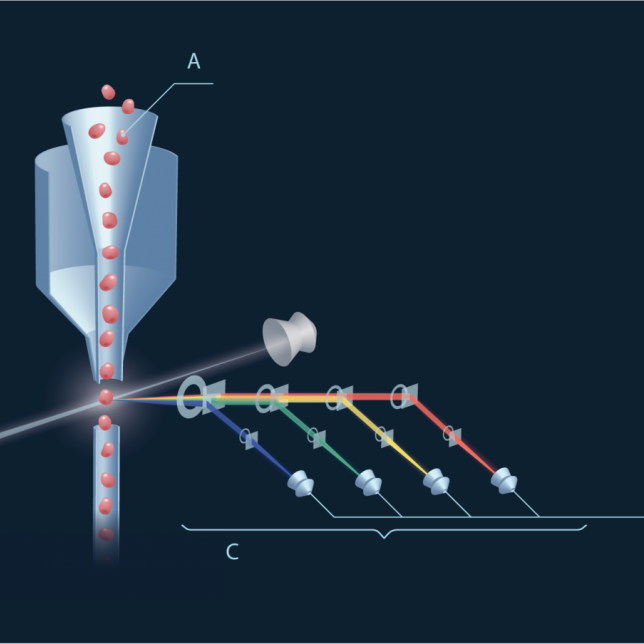
Applications of Flow Cytometry Market in Biomedical Research
Flow cytometry has become an indispensable tool in biomedical research, offering valuable insights into cellular and molecular processes. In this blog, we will explore some of the key applications of flow cytometry and its impact on advancing scientific knowledge.
Immunophenotyping: Flow cytometry enables researchers to characterize and quantify different immune cell populations based on specific surface markers. This is crucial in understanding immune responses, identifying abnormal cell populations, and studying autoimmune diseases.
Cancer Research: Flow cytometry plays a vital role in cancer research by analyzing tumor cells and assessing their characteristics. Researchers can identify cancer stem cells, study cell cycle distribution, and monitor changes in cancer cell populations during treatment.
Stem Cell Analysis: Flow cytometry is used to identify and isolate specific stem cell populations from complex tissues. This assists in regenerative medicine and understanding the cellular mechanisms governing stem cell behavior.
Apoptosis and Cell Viability Assays: Flow cytometry facilitates the assessment of cell viability and apoptosis by measuring changes in membrane integrity, mitochondrial activity, and DNA content.
The global Flow Cytometry Market is estimated to be valued at US$ 5,688.7 million in 2022 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 10.4% during the forecast period (2022-2030).
Cell Cycle Analysis: Flow cytometry allows researchers to analyze the distribution of cells across different phases of the cell cycle, providing valuable information about cell proliferation and growth.
Intracellular Protein Analysis: By using flow cytometry, researchers can detect and quantify intracellular proteins, gaining insights into cellular signaling pathways and protein interactions.
The diverse applications of Flow Cytometry Market have significantly advanced our understanding of cellular biology and disease mechanisms. As the technology continues to evolve, it holds the promise of uncovering even more complex cellular processes and accelerating biomedical research.