Introduction:
In the world of electronics and technology, the demand for faster, more powerful, and compact devices is ever-increasing. However, this pursuit of high performance comes with the inevitable consequence of generating excessive heat. Heat is the enemy of electronic components, as it can degrade their performance and shorten their lifespan. To combat this issue, Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) play a crucial role in efficiently managing heat and ensuring the optimal functioning of electronic devices. In this blog, we will explore the significance of TIMs, their types, and their applications in diverse industries.
Understanding Thermal Interface Materials:
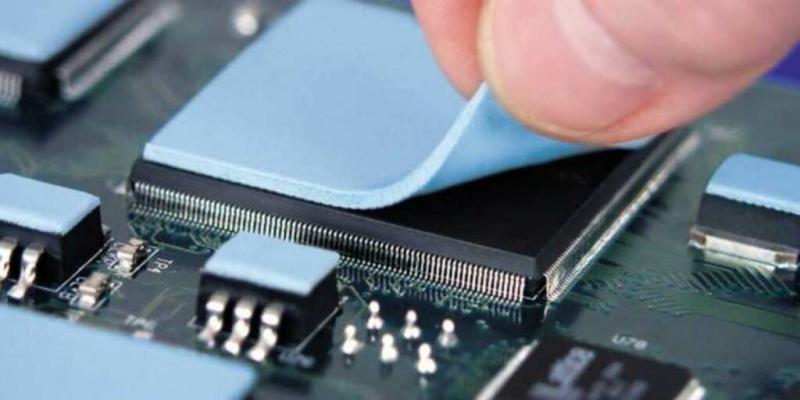
Thermal Interface Materials are substances used to enhance the heat transfer between two surfaces, such as a semiconductor device and a heat sink. The main purpose of TIMs is to fill the microscopic gaps, air pockets, and irregularities that exist between these surfaces. By doing so, they minimize thermal resistance and maximize heat dissipation efficiency. Effective heat transfer is vital for maintaining the temperature of electronic components within safe operating limits.
Types of Thermal Interface Materials:
-
Thermal Greases: These are soft, viscous materials commonly made from silicone or zinc oxide. They have a high thermal conductivity and are easy to apply. Thermal greases work by conforming to the surface irregularities, thus displacing air gaps effectively. They are widely used in various applications, including CPUs, GPUs, and power electronic devices.
-
Thermal Pads: These are pre-cut, solid sheets made from materials like silicone, graphite, or ceramic. Thermal pads are convenient to use as they don't require any additional preparation. However, their thermal conductivity is generally lower compared to thermal greases, making them more suitable for less demanding applications.
-
Thermal Adhesives: Unlike thermal greases and pads, thermal adhesives provide both thermal conduction and mechanical attachment. They are particularly useful for securing heat sinks to components permanently. Epoxies and acrylic-based adhesives are commonly used as thermal adhesives.
-
Phase Change Materials (PCM): PCM TIMs are unique as they can change their physical state based on temperature fluctuations. They offer a more consistent thermal performance by filling gaps effectively during the phase change. Waxes and greases are commonly used as PCM TIMs.
Applications of Thermal Interface Materials:
-
Computer Hardware: In the realm of computing, TIMs are essential for ensuring the effective cooling of CPUs and GPUs. High-performance gaming rigs and data centers benefit greatly from efficient TIMs as they prevent overheating and improve overall system stability.
-
Automotive Electronics: Modern vehicles are equipped with various electronic components, from infotainment systems to advanced driver assistance systems. TIMs help maintain the optimal temperature of these electronics, ensuring reliable performance and durability.
-
Power Electronics: In power electronic devices like inverters and power converters, TIMs facilitate the dissipation of heat generated during high-power operation. This enhances the efficiency and lifespan of these devices.
-
Telecommunications: In telecommunications equipment such as routers and base stations, TIMs help dissipate heat generated by high-speed data processing, ensuring consistent and uninterrupted communication.
Conclusion:
Thermal Interface Materials are integral to maintaining the longevity and reliability of electronic devices in today's technology-driven world. By effectively transferring heat from electronic components to heat sinks, TIMs play a crucial role in preventing overheating and improving overall system performance. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for more advanced and efficient TIMs will only grow. By investing in research and development, we can further optimize these materials and ensure the continued progress of the electronics industry.