Methyl Methacrylate Applications Properties Production Methods Manufacturing Trends Industrial Uses
Methyl methacrylate stands as one of the most versatile chemical compounds in modern industrial applications, serving as a fundamental building block for numerous synthetic materials and products. This colorless liquid monomer plays a crucial role in creating everything from automotive components to medical devices, making it an essential component in today's manufacturing landscape. Understanding its properties, production methods, and diverse applications provides valuable insight into the chemical industry's evolution and future directions.
Chemical Properties and Molecular Structure Characteristics
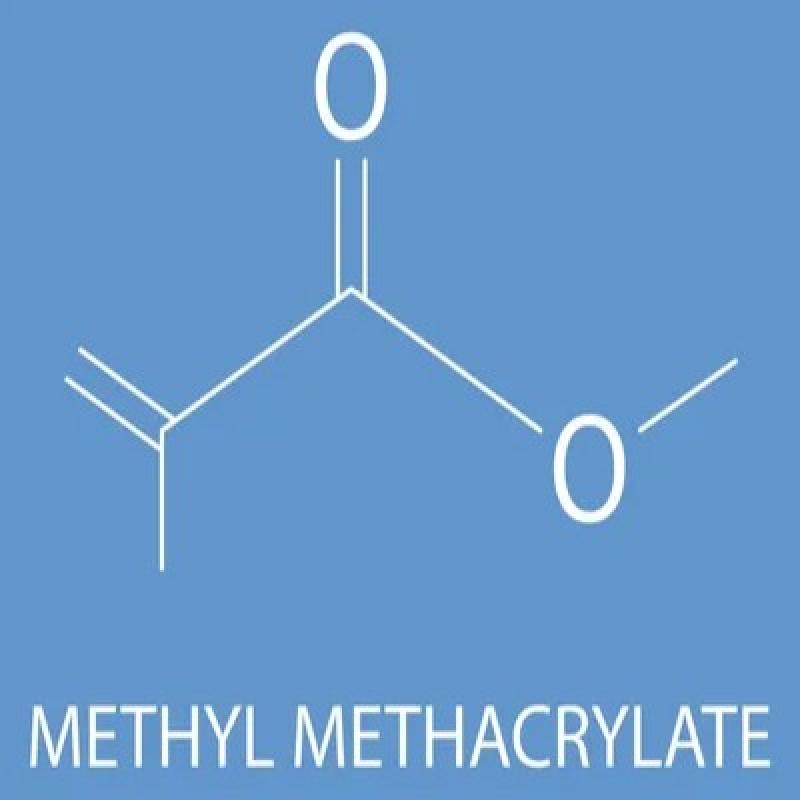
Methyl Methacrylate exhibits unique chemical properties that make it highly valuable in industrial applications. With the molecular formula C₅H₈O₂, this ester compound features a vinyl group that enables polymerization reactions, creating long-chain polymers with exceptional clarity and durability. The compound's molecular weight of 100.12 g/mol contributes to its volatility and reactivity under specific conditions.
The chemical structure includes a methyl group attached to the methacrylate backbone, providing stability while maintaining reactivity for polymerization processes. This balance allows manufacturers to control polymerization timing and conditions, resulting in materials with predictable properties. The compound's double bond configuration enables free radical polymerization, thermal polymerization, and other chemical reactions that transform the liquid monomer into solid polymeric materials.
Temperature sensitivity represents another critical characteristic, with the compound polymerizing rapidly at elevated temperatures. This property requires careful storage and handling procedures but also enables precise control during manufacturing processes. The presence of inhibitors in commercial grades prevents premature polymerization during storage and transportation, ensuring product stability throughout the supply chain.
Manufacturing Processes and Production Technologies
Modern production methods for Methyl Methacrylate involve several sophisticated chemical processes, each designed to maximize yield while maintaining product purity. The acetone cyanohydrin process remains the most widely used commercial method, involving the reaction of acetone cyanohydrin with methanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. This process produces high-purity material suitable for demanding applications while generating byproducts that can be recycled or utilized in other chemical processes.
Alternative production routes include the isobutylene oxidation process, which offers advantages in certain market conditions and raw material availability scenarios. This method involves multiple reaction steps, including oxidation, esterification, and purification stages that require precise temperature and pressure control. The resulting product meets stringent quality specifications required for high-performance applications.
Catalyst technology plays a vital role in optimizing production efficiency and product quality. Advanced catalyst systems enable lower reaction temperatures, reduced energy consumption, and improved selectivity, resulting in higher yields and reduced waste generation. Continuous process improvements focus on enhancing catalyst performance, extending catalyst life, and minimizing environmental impact through cleaner production technologies.
Quality control throughout the production process ensures consistent product specifications and performance characteristics. Analytical testing protocols monitor impurity levels, moisture content, inhibitor concentration, and other critical parameters that affect downstream processing and final product performance. These quality assurance measures maintain the reliability and consistency that industrial customers require.
Industrial Applications Across Multiple Sectors
The automotive industry represents one of the largest consumer segments, utilizing methyl methacrylate-based materials in various applications including headlight lenses, instrument panels, and exterior trim components. These applications benefit from the material's optical clarity, weather resistance, and impact strength, providing long-term durability under challenging environmental conditions. Advanced formulations enable automotive designers to create complex shapes and achieve specific performance requirements while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Electronics and technology sectors depend on methyl methacrylate derivatives for producing display screens, optical fibers, and protective coatings. The material's excellent optical properties, including high light transmission and low haze levels, make it ideal for applications requiring superior visual clarity. Additionally, its electrical insulation properties and dimensional stability support reliable performance in electronic components and assemblies.
Construction and architecture industries utilize methyl methacrylate-based materials for glazing applications, skylights, and decorative elements. The material's superior weather resistance, UV stability, and impact strength provide long-term performance advantages over traditional materials. Architectural applications benefit from the ability to create large, clear panels that maintain optical clarity throughout extended service lives while withstanding environmental stresses.
Medical and healthcare applications leverage the biocompatibility and sterilization resistance of properly formulated methyl methacrylate materials. These properties enable use in medical devices, pharmaceutical packaging, and laboratory equipment where cleanliness and safety are paramount. The material's chemical resistance and ease of cleaning support stringent hygiene requirements in healthcare environments.
Get This Report in Japanese Language: メタクリル酸メチル
Get This Report in Korean Language: 메틸 메타크릴레이트
Read More Articles Related to this Industry- The Role of Methyl Methacrylate In Acrylic Sheets
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)