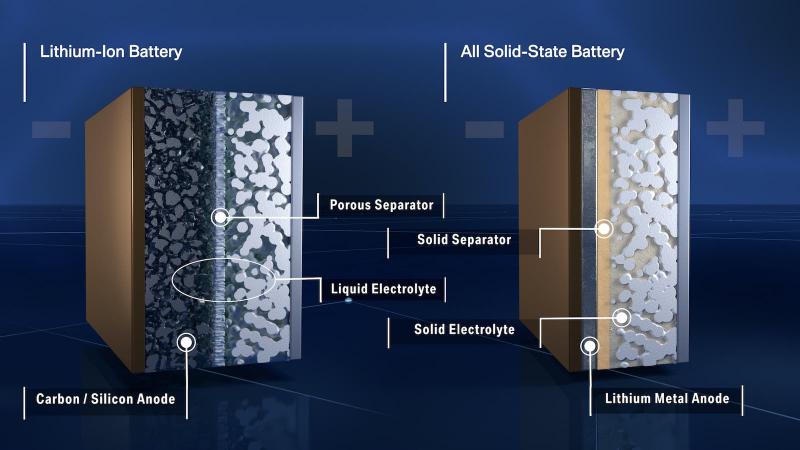
In the quest for cleaner and more efficient energy storage solutions, solid-state batteries have emerged as a groundbreaking technology with the potential to revolutionize the way we power our world. These batteries offer a promising alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries, promising enhanced safety, higher energy density, and longer lifespan.
At the heart of the solid-state battery lies its fundamental difference from conventional lithium-ion batteries: the electrolyte. Instead of using liquid electrolytes, which are prone to leakage and thermal runaway, solid-state batteries employ solid electrolytes. These solid electrolytes, typically ceramic or polymer-based, conduct lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes, offering improved stability and safety.
One of the primary advantages of solid-state batteries is their enhanced safety profile. By eliminating flammable liquid electrolytes, the risk of fire and explosion is significantly reduced, making them inherently safer for use in various applications. This newfound safety is particularly critical for electric vehicles, where concerns about battery fires have been a significant roadblock to mass adoption.
Additionally, solid-state batteries promise higher energy densities, meaning they can store more energy in the same volume compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This property opens up exciting possibilities for electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and other portable electronic devices, where longer battery life and faster charging times are highly sought after.
Another area where solid-state batteries shine is in their longevity. The solid electrolytes exhibit minimal degradation over time, leading to a longer lifespan for the batteries. This translates to reduced waste generation and a more sustainable energy storage solution, aligning with the global push towards environmental consciousness.
While solid-state batteries offer numerous advantages, their commercialization and widespread adoption have faced challenges. Manufacturing solid-state batteries at scale has proven to be a complex and expensive process, hindering their integration into mainstream markets. Researchers and companies in the energy storage sector are actively working to overcome these barriers and optimize the production processes to make solid-state batteries more economically viable.
The potential of solid-state batteries goes beyond consumer electronics and electric vehicles. These batteries could play a significant role in grid-level energy storage, making renewable energy sources such as wind and solar more feasible and reliable. By storing excess energy during peak generation periods and releasing it when demand is high, solid-state batteries can contribute to a more stable and sustainable energy grid.