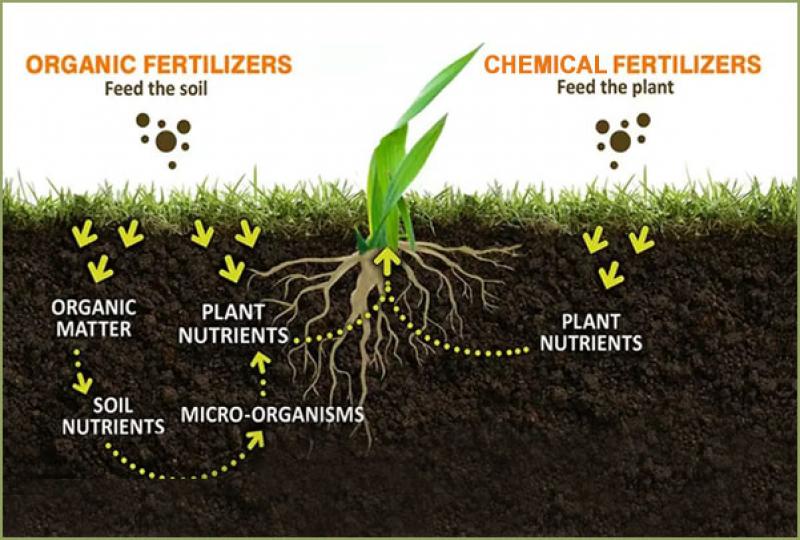
Organic fertilizers are plant or animal-based substances that provide essential nutrients to plants. These fertilizers are typically rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with other micro and macronutrients necessary for plant growth. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, organic variants are minimally processed, allowing them to retain a diverse array of nutrients that are gradually released into the soil as the organic matter decomposes.
Advantages of Organic Fertilizers
Environmental Sustainability: Organic fertilizers are biodegradable and do not contribute to soil or water pollution. They enhance soil structure and water retention capacity, reducing the risk of erosion and runoff.
Soil Health: Organic fertilizers improve soil fertility by promoting beneficial microbial activity. This, in turn, enhances nutrient availability to plants and supports a balanced ecosystem below the ground.
Nutrient Efficiency: The nutrients in organic fertilizers are released slowly over time, providing a steady and sustained supply to plants. This reduces nutrient leaching and wastage, making the most of the applied fertilizers.
Non-Toxic: Organic fertilizers do not contain harmful chemicals, making them safe for farmers, consumers, and the environment. They also help maintain the purity of groundwater and prevent the buildup of toxic residues in crops.
Long-Term Benefits: By nourishing the soil and improving its structure, organic fertilizers contribute to long-term agricultural productivity, unlike synthetic fertilizers, which may lead to soil degradation over time.
Types of Organic Fertilizers
There is a wide range of organic fertilizers available, each with its unique composition and benefits:
Compost: Compost is one of the most popular organic fertilizers, made by decomposing organic waste such as kitchen scraps, yard trimmings, and manure. It enriches the soil with nutrients and improves its ability to retain moisture.
Manure: Animal manure, when properly composted, serves as an excellent source of organic nutrients. It is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and helps fortify the soil's microbial activity.
Bone Meal: Derived from animal bones, bone meal is a phosphorus-rich organic fertilizer that promotes robust root development and flowering in plants.
Fish Emulsion: This liquid fertilizer is made from fish waste and is a quick-release source of nitrogen, making it ideal for providing an immediate nutrient boost to plants.
Seaweed and Kelp: Extracts from seaweed and kelp are rich in micronutrients, growth hormones, and beneficial plant compounds that enhance overall plant health and resilience.
Implementing Organic Fertilizers in Agriculture
Integrating organic fertilizers into conventional farming practices requires careful planning and consideration. Farmers need to assess their soil's nutrient requirements, choose the appropriate organic fertilizers, and adopt sustainable application techniques. Crop rotation, cover cropping, and green manure practices further support the efficacy of organic fertilizers, contributing to soil fertility and reducing the reliance on synthetic inputs.
Conclusion
Organic fertilizers offer a sustainable pathway to nourishing crops, revitalizing soil health, and safeguarding the environment. As the world seeks solutions to the challenges of modern agriculture, the adoption of organic fertilizers represents a promising step towards a more sustainable and resilient food production system. By harnessing the power of nature, organic fertilizers support the delicate balance between human needs and ecological preservation, ultimately paving the way for a greener and healthier future.