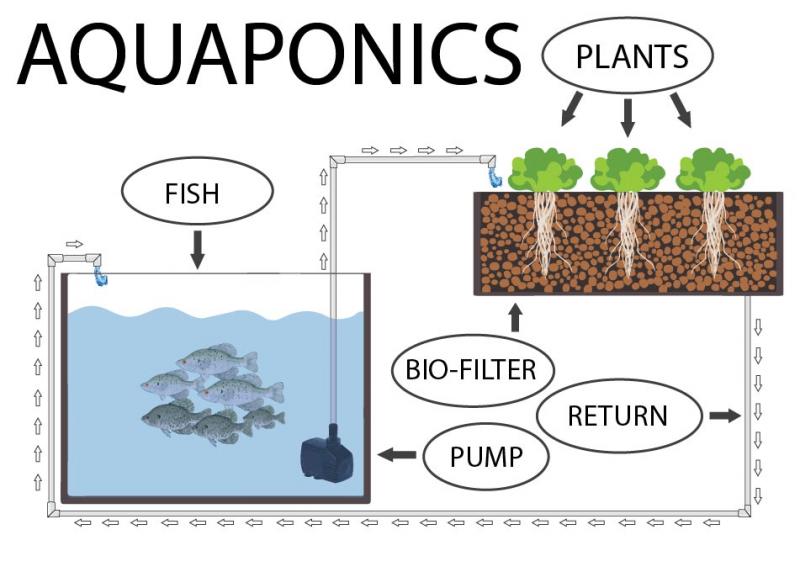
Aquaponics is a cutting-edge agricultural technique that combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) into a single, sustainable system. This innovative approach to farming has gained significant popularity in recent years due to its efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and ability to produce both fish and vegetables simultaneously. By creating a harmonious ecosystem where fish waste is converted into nutrients for plants, aquaponics offers a holistic solution for modern agriculture.
How Aquaponics Works
At the heart of aquaponics lies the concept of symbiosis between fish and plants. The system starts with a fish tank, where aquatic species such as tilapia, trout, or catfish are raised. As the fish consume food, they excrete waste rich in ammonia. In a conventional fish farm, this waste would be a pollutant, but in an aquaponics setup, it becomes a valuable resource.
The fish waste is carried to the second component of the system: the hydroponic grow beds. These beds contain a medium, like clay pebbles or gravel, where plants grow without soil. Beneficial bacteria in the grow beds convert the ammonia from the fish waste into nitrates and nitrites. These compounds serve as essential nutrients for the plants.
As the plants uptake these nutrients, they purify the water, removing harmful substances for the fish. The clean water is then recirculated back into the fish tank, completing the cycle.
Benefits of Aquaponics
Water Efficiency: Aquaponics uses a fraction of the water compared to traditional farming methods. The water is continually recycled, making it possible to grow crops in areas with limited water resources.
Reduced Environmental Impact: Since aquaponics relies on natural processes and eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, it significantly reduces the release of harmful chemicals into the environment.
Year-Round Production: Aquaponic systems can be set up indoors or in controlled environments, allowing year-round crop production regardless of external weather conditions.
Space-Efficient: Aquaponics can be implemented vertically or in compact setups, making it suitable for urban areas or places with limited land.
Diverse Harvest: Farmers can simultaneously yield fresh fish and a variety of vegetables, providing a balanced and nutritious harvest.
Challenges and Considerations
While aquaponics offers numerous advantages, it also comes with its challenges. Proper system balance, fish and plant selection, and water quality management are crucial to ensure the system's success. Additionally, initial setup costs can be relatively high, but long-term savings on water and fertilizers offset the investment.
Conclusion
Aquaponics represents a promising frontier in sustainable agriculture, presenting an environmentally friendly and resource-efficient method of food production. With ongoing advancements and increased awareness, aquaponics has the potential to play a vital role in food security and ecosystem preservation for a more sustainable future. As more individuals and communities adopt this technology, the world may see a significant transformation in the way we grow and consume food.